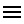Fnc
Used to express function types, or to define or declare functions.
fnc ([argTy<type>...]) retTy<type or ()> -> type
Expresses a function type of given argument types and return type.
If a type retTy is provided, that will be the return type. Otherwise, the function type is of a non-returning function.
sym f0:(fnc (i32) ()) f1:(fnc (f32 f32) f32);
::variadic on the argument types node expresses a variadic function.
::noDrop on argTy marks the argument as non-owning.
fnc name<id> ([arg<id:type>...]) retTy<type or ()> -> function
fnc name<id> ([arg<id:type>...]) retTy<type or ()> body<block> -> function
Declares of defines a function under the given name. Returns that function.
If body isn’t provided, this instruction declares a function.
There must not be a macro, special form, type, or global symbol with the same. The name must not be one of cn, *, or [].
There must not be multiple arguments of the same name.
If a type retTy is provided, that will be the return type. If it is a type, this is a returning function and is expected to return a value of that type after it finishes execution.
Argument types and the return type must not be undefined types if this is a function definition.
When executing, the function will execute the list of instructions in body under a new scope.
It is allowed to overload functions of the same name. There must not be conflicting function definitions among them. All functions declarations and the definition (where there is one) of the same signature must be conforming.
fnc sqrt (x:f32) f32;
fnc sqrt (x:f64) f64;
fnc square (x:f32) f32 { ret (* x x); };
fnc square (x:f64) f64 { ret (* x x); };
::global must be placed on fnc if this instruction is not executed in the global scope.
::noNameMangle on name forces the compiler to not mangle the name of the compiled function. If name mangling is disabled, overloading is not allowed. Functions named main and variadic functions always have name mangling disabled.
::evaluable on name makes this an evaluated function. By default, a function is evaluated if it is defined through evaluation.
::compilable on name makes this a compiled function. By default, a function is evaluated if it is defined through compilation.
Functions must not be marked as neither evaluable nor compilable.
::variadic on the arguments node makes this a variadic function.
::noDrop on argTy marks the argument as non-owning.